Key Insights
The New Zealand infrastructure industry is poised for steady growth, with an estimated market size of $14.5 billion in 2022 and a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 3% through to 2033. This expansion is underpinned by robust government investment and a clear focus on upgrading and expanding critical public and private sector assets. Key drivers include the ongoing need to modernize aging transportation networks, enhance energy generation and distribution capabilities, and develop social infrastructure to support a growing population. Significant investment in roading projects, public transport upgrades in major urban centers like Auckland and Wellington, and the expansion of renewable energy sources are at the forefront of this growth. The government's commitment to sustainable development and climate resilience further fuels demand for infrastructure projects that incorporate green technologies and disaster preparedness.
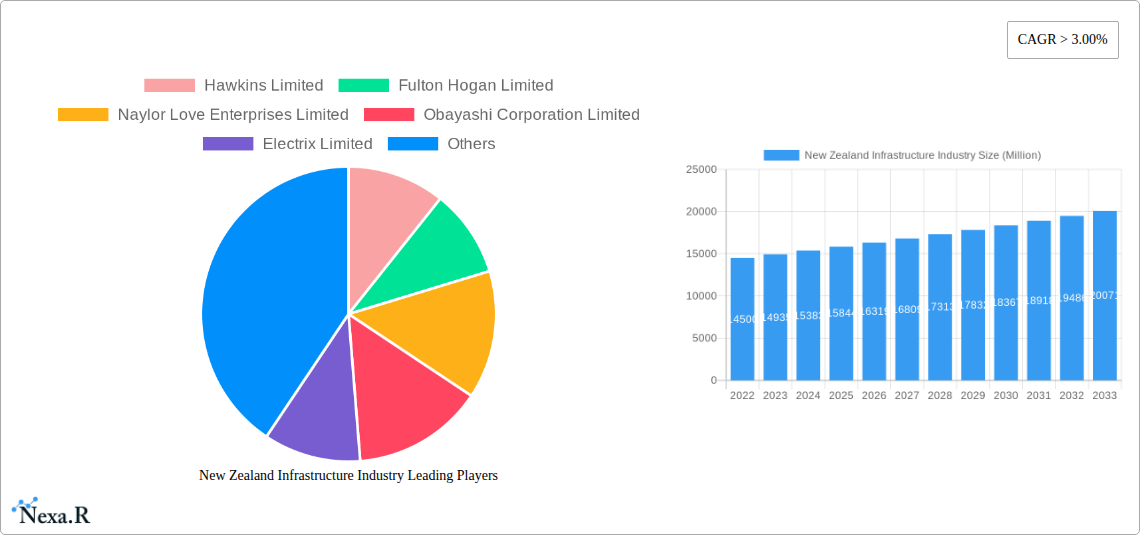
New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Market Size (In Billion)

While the market presents significant opportunities, it also faces certain restraints. These include the availability of skilled labor, which can impact project timelines and costs, and potential supply chain disruptions, particularly for specialized materials and equipment. However, the industry is actively addressing these challenges through training initiatives and diversified sourcing strategies. Segmentation analysis reveals strong performance across social infrastructure, particularly in healthcare and education facilities, and substantial activity within the transportation sector. The ongoing development of digital infrastructure, including enhanced telecommunications networks, is also a notable trend. Major companies like Hawkins Limited, Fulton Hogan Limited, and Downer Group are actively participating in this dynamic market, contributing to its overall expansion and evolution.
New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Company Market Share

New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Market Dynamics & Structure
The New Zealand infrastructure industry is characterized by a dynamic market structure influenced by government spending, private sector investment, and technological advancements. Market concentration varies across segments, with some dominated by large, established players and others offering more diverse opportunities. Major companies like Hawkins Limited, Fulton Hogan Limited, and Downer Group hold significant market share, particularly in transportation and social infrastructure projects. Technological innovation is a key driver, with advancements in sustainable construction materials, digital twin technology for asset management, and smart city solutions reshaping project delivery and operational efficiency. The regulatory framework, governed by entities like the Ministry of Infrastructure and regional councils, sets standards for project approvals, environmental impact assessments, and procurement processes, directly influencing market entry and competition. Competitive product substitutes are less prevalent in core infrastructure development, but innovation in materials and construction techniques can offer more cost-effective or sustainable alternatives. End-user demographics are shifting, with an increasing demand for resilient infrastructure to withstand climate change impacts and an aging population requiring enhanced social infrastructure. Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) trends indicate consolidation in certain segments, as companies seek to expand their capabilities and market reach.
- Market Concentration: Varies by segment, with transportation and social infrastructure showing higher concentration from major players.
- Technological Innovation Drivers: Sustainability, digitalization, smart city solutions, advanced materials.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Government policies, environmental standards, procurement regulations.
- Competitive Product Substitutes: Primarily in material innovation and construction methodologies.
- End-User Demographics: Demand for climate-resilient, accessible, and technologically integrated infrastructure.
- M&A Trends: Consolidation for capability expansion and market share growth.
New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Growth Trends & Insights
The New Zealand infrastructure industry is poised for substantial growth, driven by an increasing need for modernization, expansion, and climate resilience. The market size is projected to see a significant upward trajectory, fueled by both public and private sector investments aiming to address existing deficits and prepare for future demands. From a historical perspective, the period from 2019 to 2024 has seen steady investment, laying the groundwork for the anticipated expansion. The base year of 2025 marks a pivotal point, with an estimated market value of $55.6 billion, reflecting ongoing project commitments and emerging opportunities. This figure is expected to climb significantly throughout the forecast period of 2025–2033.
Adoption rates for new technologies and sustainable practices are steadily increasing. This includes the widespread integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) for enhanced project planning and execution, the adoption of prefabrication and modular construction to accelerate timelines and reduce waste, and a growing emphasis on green infrastructure solutions such as renewable energy projects and sustainable water management systems. These technological disruptions are not only improving the efficiency and sustainability of infrastructure development but are also reshaping the entire project lifecycle, from design to maintenance.
Consumer behavior shifts are playing a crucial role, with a heightened public expectation for reliable, accessible, and environmentally conscious infrastructure. This translates into increased demand for public transportation networks, affordable housing, advanced telecommunications, and robust utility services. The growing awareness of climate change is also driving demand for resilient infrastructure capable of withstanding extreme weather events, leading to increased investment in flood defenses, upgraded road and rail networks, and secure energy grids. The market penetration of digitally enabled infrastructure services, such as smart traffic management systems and connected utility networks, is also on the rise, further contributing to market expansion. The projected CAGR for the New Zealand infrastructure market is xx%, indicating a robust growth trajectory. This evolution reflects a strategic pivot towards a more sustainable, digitally integrated, and citizen-centric approach to infrastructure development, ensuring the industry remains a cornerstone of the nation's economic and social progress.
Dominant Regions, Countries, or Segments in New Zealand Infrastructure Industry
The New Zealand infrastructure industry is experiencing robust growth, with Transportation Infrastructure emerging as a dominant segment, particularly driven by significant investments in Roadways and Railways. Key cities such as Auckland and Wellington are at the forefront of this expansion, acting as hubs for major transport projects that are crucial for economic connectivity and urban development. The nation's ongoing commitment to improving its transportation networks is a direct response to population growth, increasing freight demands, and the strategic imperative to decarbonize the transport sector.
In the Transportation Infrastructure segment, Roadways constitute a substantial portion of the market. Investments in highway upgrades, new arterial routes, and urban congestion relief projects are prevalent across the country. These projects are essential for facilitating the movement of goods and people, supporting economic activity, and enhancing regional connectivity. For instance, projects aimed at improving State Highways and local road networks are critical for businesses and commuters alike.
Railways are also witnessing considerable attention, with significant investment in upgrading existing lines, expanding commuter services, and developing new freight corridors. The push towards sustainable transportation solutions has revitalized the rail sector, positioning it as a key component of the nation's decarbonization strategy. Projects like the City Rail Link in Auckland are transforming urban mobility and demonstrating the growing importance of rail infrastructure.
Auckland, as New Zealand's largest city and economic powerhouse, consistently leads in infrastructure investment. Its population density and economic activity necessitate continuous development across all infrastructure segments. The city is a focal point for major transportation projects, including airport expansions and upgrades to its public transport network. Wellington, the capital, also commands significant infrastructure spending, with a focus on enhancing its public transport, roading, and social infrastructure to support its role as a government and administrative center. Hamilton, a growing urban center, is also experiencing increased infrastructure development, particularly in transportation and social infrastructure, to accommodate its expanding population and economic base.
The dominance of Transportation Infrastructure is further bolstered by government policies prioritizing its development for economic growth, job creation, and improved quality of life. The lifecycle of these projects, from planning and construction to maintenance, creates sustained economic activity and employment opportunities. Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies in transportation, such as intelligent traffic management systems and connected vehicle infrastructure, is enhancing the efficiency and appeal of this segment. The market share of Transportation Infrastructure within the overall New Zealand infrastructure market is estimated to be xx billion units.
New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Product Landscape
The New Zealand infrastructure industry is witnessing a surge in product innovation, driven by the demand for sustainable, resilient, and technologically advanced solutions. Companies are focusing on developing and deploying advanced construction materials that offer enhanced durability, reduced environmental impact, and faster installation times. This includes innovative concrete formulations, sustainable timber products, and recyclable materials. Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies is transforming the product landscape, with the adoption of sensors, IoT devices, and advanced analytics for infrastructure monitoring, management, and predictive maintenance. Applications span across all infrastructure segments, from smart road systems that optimize traffic flow to intelligent buildings equipped with energy-efficient systems and advanced security features. Performance metrics are increasingly centered on lifecycle cost, environmental footprint, and operational efficiency, pushing the boundaries of what traditional infrastructure can achieve.
Key Drivers, Barriers & Challenges in New Zealand Infrastructure Industry
Key Drivers: The New Zealand infrastructure industry is propelled by a confluence of robust economic growth, a burgeoning population necessitating expanded services, and a significant government commitment to modernization and climate resilience. Technological advancements, particularly in sustainable construction and digital integration, are key accelerators. Investments in renewable energy, decarbonization initiatives, and the development of smart city solutions are driving innovation and market expansion. Furthermore, strategic public-private partnerships are crucial for mobilizing capital and expertise for large-scale projects.
Barriers & Challenges: Despite strong growth prospects, the industry faces significant challenges. Supply chain disruptions and material shortages can lead to project delays and cost overruns, exacerbated by global economic factors. The scarcity of skilled labor remains a persistent issue, impacting project timelines and quality. Navigating complex regulatory frameworks and lengthy consenting processes can also act as a restraint. Fierce competition among a limited number of large players can sometimes lead to price pressures. Furthermore, the substantial capital investment required for major infrastructure projects poses a continuous challenge for financing and resource allocation. The estimated impact of these challenges on project timelines can be up to xx%.
Emerging Opportunities in New Zealand Infrastructure Industry
Emerging opportunities in the New Zealand infrastructure industry are largely centered around the transition to a low-carbon economy and the adaptation to climate change. This includes significant investment potential in renewable energy generation and transmission, such as offshore wind farms and enhanced grid infrastructure. The development of sustainable transport solutions, including electric vehicle charging networks and expanded public transport systems, presents a growing market. The demand for climate-resilient infrastructure, such as upgraded flood defenses, coastal protection measures, and drought-resistant water systems, is creating new avenues for innovation and development. Furthermore, the increasing focus on digital infrastructure, including 5G rollout and the development of smart city technologies, offers substantial growth prospects.
Growth Accelerators in the New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Industry
The long-term growth of the New Zealand infrastructure industry is being significantly accelerated by groundbreaking technological breakthroughs, particularly in the fields of green construction materials, advanced digital twin technology for asset management, and smart grid solutions for energy distribution. Strategic partnerships between government agencies, private enterprises, and international technology providers are crucial for fostering innovation and facilitating the adoption of these cutting-edge solutions. Market expansion strategies, including a renewed focus on regional development and the integration of infrastructure projects with broader economic and social objectives, are also acting as powerful catalysts for sustained growth.
Key Players Shaping the New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Market
- Hawkins Limited
- Fulton Hogan Limited
- Naylor Love Enterprises Limited
- Obayashi Corporation Limited
- Electrix Limited
- Visionstream Pty Limited
- Cpb Contractors Pty Limited
- City Care Limited
- Kiwi Property Group Limited
- Downer Group
Notable Milestones in New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Sector
- 2021 May: City Rail Link (Auckland) receives significant funding boost, accelerating its construction timeline for urban transport enhancement.
- 2022 March: Downer Group awarded major road maintenance contract in North Island, highlighting ongoing investment in transportation networks.
- 2022 August: Government announces $2 billion investment in renewable energy projects, boosting the extraction and energy infrastructure segments.
- 2023 February: Hawkins Limited secures contract for new hospital wing in Christchurch, demonstrating continued focus on social infrastructure development.
- 2023 October: Fulton Hogan Limited leads consortium for new expressway development in South Island, improving regional connectivity.
- 2024 January: Electrix Limited completes upgrade of critical electricity transmission lines, enhancing energy grid reliability.
In-Depth New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Market Outlook
The New Zealand infrastructure industry is set for robust and sustained growth, driven by an accelerating commitment to sustainability, digital transformation, and climate resilience. The market outlook is characterized by a strong pipeline of projects across social, transportation, and extraction infrastructure, supported by proactive government policies and increasing private sector investment. Strategic partnerships and technological innovation will continue to be key enablers, driving efficiency and the adoption of future-ready solutions. Untapped markets in regional development and the expansion of smart city ecosystems present significant future opportunities, promising continued expansion and value creation within the industry.
New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Segmentation
-
1. Infrastructure segment
-
1.1. Social Infrastructure
- 1.1.1. Schools
- 1.1.2. Hospitals
- 1.1.3. Defence
- 1.1.4. Other Social Infrastructures
-
1.2. Transportation Infrastructure
- 1.2.1. Railways
- 1.2.2. Roadways
- 1.2.3. Airports
- 1.2.4. Waterways
-
1.3. Extraction Infrastructure
- 1.3.1. Power Generation
- 1.3.2. Electricity Transmission and Distribution
- 1.3.3. Gas
- 1.3.4. Telecoms
-
1.4. Manufacturing Infrastructure
- 1.4.1. Metal and Ore Production
- 1.4.2. Petroleum Refining
- 1.4.3. Chemical Manufacturing
- 1.4.4. Industrial Parks and Clusters
- 1.4.5. Other Manufacturing Infrastructures
-
1.1. Social Infrastructure
-
2. Key Cities
- 2.1. Wellington
- 2.2. Auckland
- 2.3. Hamilton
New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Segmentation By Geography
- 1. New Zealand
New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Regional Market Share

Geographic Coverage of New Zealand Infrastructure Industry
New Zealand Infrastructure Industry REPORT HIGHLIGHTS
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2020-2034 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Estimated Year | 2026 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 3% from 2020-2034 |
| Segmentation |
|
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 1.1. Research Scope
- 1.2. Market Segmentation
- 1.3. Research Methodology
- 1.4. Definitions and Assumptions
- 2. Executive Summary
- 2.1. Introduction
- 3. Market Dynamics
- 3.1. Introduction
- 3.2. Market Drivers
- 3.2.1. Growth of Education Sector; Rising Demand for Quality Accomodation
- 3.3. Market Restrains
- 3.3.1. Enrolment Fluctuations
- 3.4. Market Trends
- 3.4.1. Increasing Demand for Transport Infrastructure Driving the Market
- 4. Market Factor Analysis
- 4.1. Porters Five Forces
- 4.2. Supply/Value Chain
- 4.3. PESTEL analysis
- 4.4. Market Entropy
- 4.5. Patent/Trademark Analysis
- 5. New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Analysis, Insights and Forecast, 2020-2032
- 5.1. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Infrastructure segment
- 5.1.1. Social Infrastructure
- 5.1.1.1. Schools
- 5.1.1.2. Hospitals
- 5.1.1.3. Defence
- 5.1.1.4. Other Social Infrastructures
- 5.1.2. Transportation Infrastructure
- 5.1.2.1. Railways
- 5.1.2.2. Roadways
- 5.1.2.3. Airports
- 5.1.2.4. Waterways
- 5.1.3. Extraction Infrastructure
- 5.1.3.1. Power Generation
- 5.1.3.2. Electricity Transmission and Distribution
- 5.1.3.3. Gas
- 5.1.3.4. Telecoms
- 5.1.4. Manufacturing Infrastructure
- 5.1.4.1. Metal and Ore Production
- 5.1.4.2. Petroleum Refining
- 5.1.4.3. Chemical Manufacturing
- 5.1.4.4. Industrial Parks and Clusters
- 5.1.4.5. Other Manufacturing Infrastructures
- 5.1.1. Social Infrastructure
- 5.2. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Key Cities
- 5.2.1. Wellington
- 5.2.2. Auckland
- 5.2.3. Hamilton
- 5.3. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Region
- 5.3.1. New Zealand
- 5.1. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Infrastructure segment
- 6. Competitive Analysis
- 6.1. Market Share Analysis 2025
- 6.2. Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Hawkins Limited
- 6.2.1.1. Overview
- 6.2.1.2. Products
- 6.2.1.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.1.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.1.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.2 Fulton Hogan Limited
- 6.2.2.1. Overview
- 6.2.2.2. Products
- 6.2.2.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.2.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.2.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.3 Naylor Love Enterprises Limited
- 6.2.3.1. Overview
- 6.2.3.2. Products
- 6.2.3.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.3.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.3.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.4 Obayashi Corporation Limited
- 6.2.4.1. Overview
- 6.2.4.2. Products
- 6.2.4.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.4.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.4.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.5 Electrix Limited
- 6.2.5.1. Overview
- 6.2.5.2. Products
- 6.2.5.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.5.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.5.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.6 Visionstream Pty Limited*List Not Exhaustive
- 6.2.6.1. Overview
- 6.2.6.2. Products
- 6.2.6.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.6.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.6.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.7 Cpb Contractors Pty Limited
- 6.2.7.1. Overview
- 6.2.7.2. Products
- 6.2.7.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.7.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.7.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.8 City Care Limited
- 6.2.8.1. Overview
- 6.2.8.2. Products
- 6.2.8.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.8.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.8.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.9 Kiwi Property Group Limited
- 6.2.9.1. Overview
- 6.2.9.2. Products
- 6.2.9.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.9.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.9.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.10 Downer Group
- 6.2.10.1. Overview
- 6.2.10.2. Products
- 6.2.10.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.10.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.10.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.1 Hawkins Limited
List of Figures
- Figure 1: New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Revenue Breakdown (undefined, %) by Product 2025 & 2033
- Figure 2: New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Share (%) by Company 2025
List of Tables
- Table 1: New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Revenue undefined Forecast, by Infrastructure segment 2020 & 2033
- Table 2: New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Revenue undefined Forecast, by Key Cities 2020 & 2033
- Table 3: New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Revenue undefined Forecast, by Region 2020 & 2033
- Table 4: New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Revenue undefined Forecast, by Infrastructure segment 2020 & 2033
- Table 5: New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Revenue undefined Forecast, by Key Cities 2020 & 2033
- Table 6: New Zealand Infrastructure Industry Revenue undefined Forecast, by Country 2020 & 2033
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of the New Zealand Infrastructure Industry?
The projected CAGR is approximately 3%.
2. Which companies are prominent players in the New Zealand Infrastructure Industry?
Key companies in the market include Hawkins Limited, Fulton Hogan Limited, Naylor Love Enterprises Limited, Obayashi Corporation Limited, Electrix Limited, Visionstream Pty Limited*List Not Exhaustive, Cpb Contractors Pty Limited, City Care Limited, Kiwi Property Group Limited, Downer Group.
3. What are the main segments of the New Zealand Infrastructure Industry?
The market segments include Infrastructure segment, Key Cities.
4. Can you provide details about the market size?
The market size is estimated to be USD XXX N/A as of 2022.
5. What are some drivers contributing to market growth?
Growth of Education Sector; Rising Demand for Quality Accomodation.
6. What are the notable trends driving market growth?
Increasing Demand for Transport Infrastructure Driving the Market.
7. Are there any restraints impacting market growth?
Enrolment Fluctuations.
8. Can you provide examples of recent developments in the market?
N/A
9. What pricing options are available for accessing the report?
Pricing options include single-user, multi-user, and enterprise licenses priced at USD 3800, USD 4500, and USD 5800 respectively.
10. Is the market size provided in terms of value or volume?
The market size is provided in terms of value, measured in N/A.
11. Are there any specific market keywords associated with the report?
Yes, the market keyword associated with the report is "New Zealand Infrastructure Industry," which aids in identifying and referencing the specific market segment covered.
12. How do I determine which pricing option suits my needs best?
The pricing options vary based on user requirements and access needs. Individual users may opt for single-user licenses, while businesses requiring broader access may choose multi-user or enterprise licenses for cost-effective access to the report.
13. Are there any additional resources or data provided in the New Zealand Infrastructure Industry report?
While the report offers comprehensive insights, it's advisable to review the specific contents or supplementary materials provided to ascertain if additional resources or data are available.
14. How can I stay updated on further developments or reports in the New Zealand Infrastructure Industry?
To stay informed about further developments, trends, and reports in the New Zealand Infrastructure Industry, consider subscribing to industry newsletters, following relevant companies and organizations, or regularly checking reputable industry news sources and publications.
Methodology
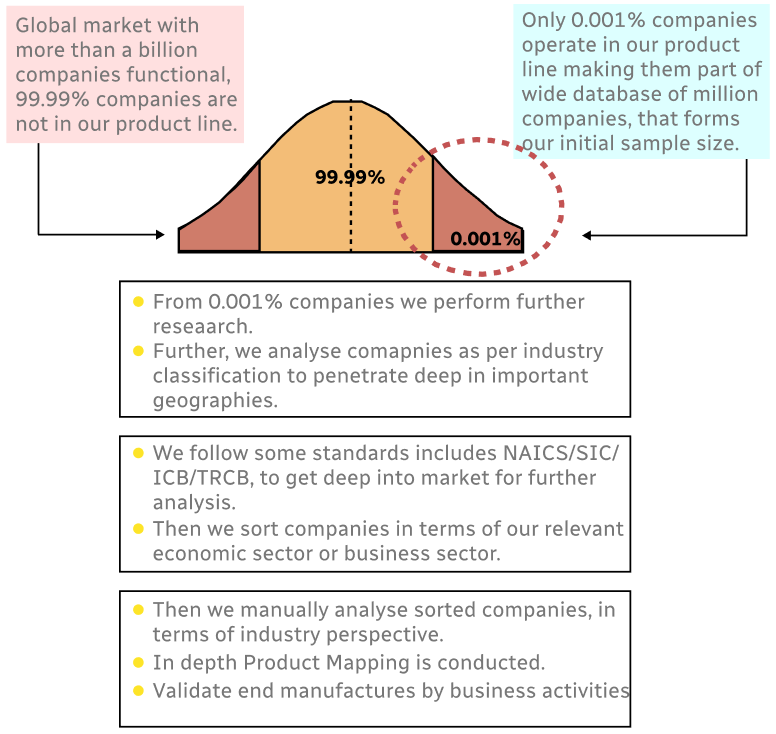
Step 1 - Identification of Relevant Samples Size from Population Database
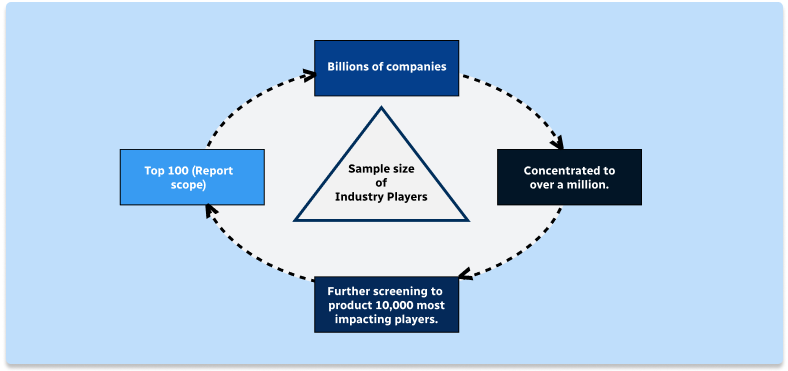
Step 2 - Approaches for Defining Global Market Size (Value, Volume* & Price*)
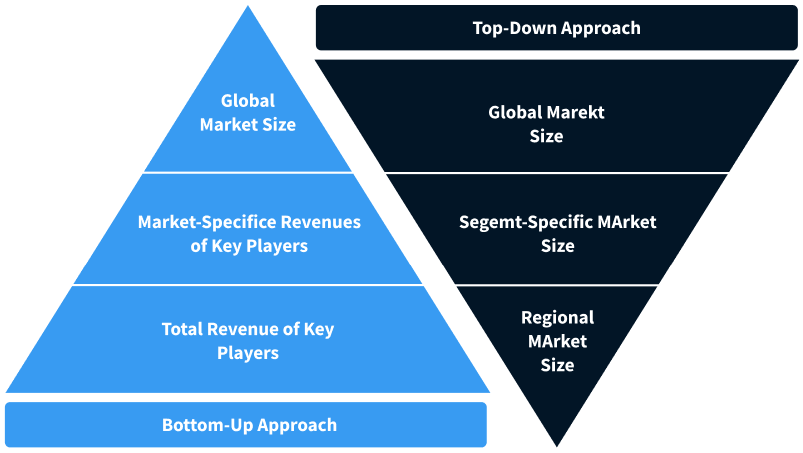
Note*: In applicable scenarios
Step 3 - Data Sources
Primary Research
- Web Analytics
- Survey Reports
- Research Institute
- Latest Research Reports
- Opinion Leaders
Secondary Research
- Annual Reports
- White Paper
- Latest Press Release
- Industry Association
- Paid Database
- Investor Presentations
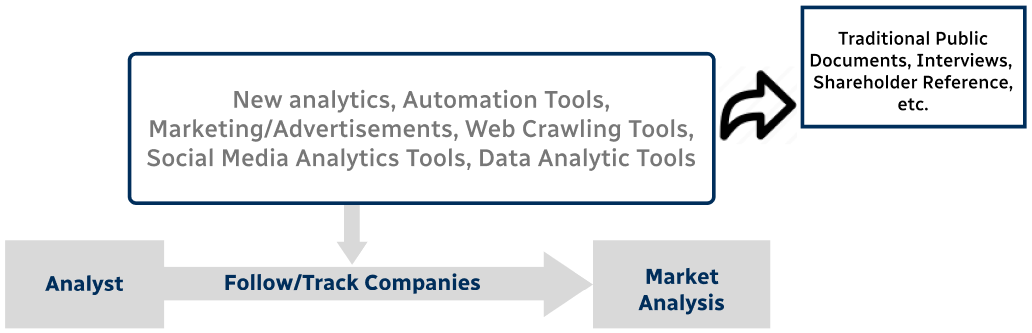
Step 4 - Data Triangulation
Involves using different sources of information in order to increase the validity of a study
These sources are likely to be stakeholders in a program - participants, other researchers, program staff, other community members, and so on.
Then we put all data in single framework & apply various statistical tools to find out the dynamic on the market.
During the analysis stage, feedback from the stakeholder groups would be compared to determine areas of agreement as well as areas of divergence


